François Jacob and Jacques Monod transformed our understanding of genetics and laid the foundations of modern biology. Their work in the field of messenger RNA (mRNA, ( mRNA ) not only unravelled the mysteries of gene expression, it also not only unlocked the mysteries of gene expression, but also contributed to the explanation of how protein production in cells is regulated . protein production in cellsis regulated.
The Historical Context
During the 1950s and 1960s, scientists were beginning to understand how the genetic information contained in DNA is translated into the proteins that perform most cellular functions. Jacob and Monod, working at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, focused on studying gene regulation in bacteria, specifically Escherichia coli. It was in this model system that they made their most important discovery: mRNA. In simple terms, mRNA acts as an intermediary that carries genetic information from the DNA to the cell’s ribosome, the organelle where proteins are synthesised. Jacob and Monod’s work led to the development of the ‘operon hypothesis’ model, which explains how gene expression is regulated in bacteria. This model proposes that genes involved in a specific process are grouped into operons, and that a single mRNA message can encode multiple related proteins. This concept was fundamental to understanding how cells coordinate protein production in response to different environmental conditions.
The lac operon and gene regulation
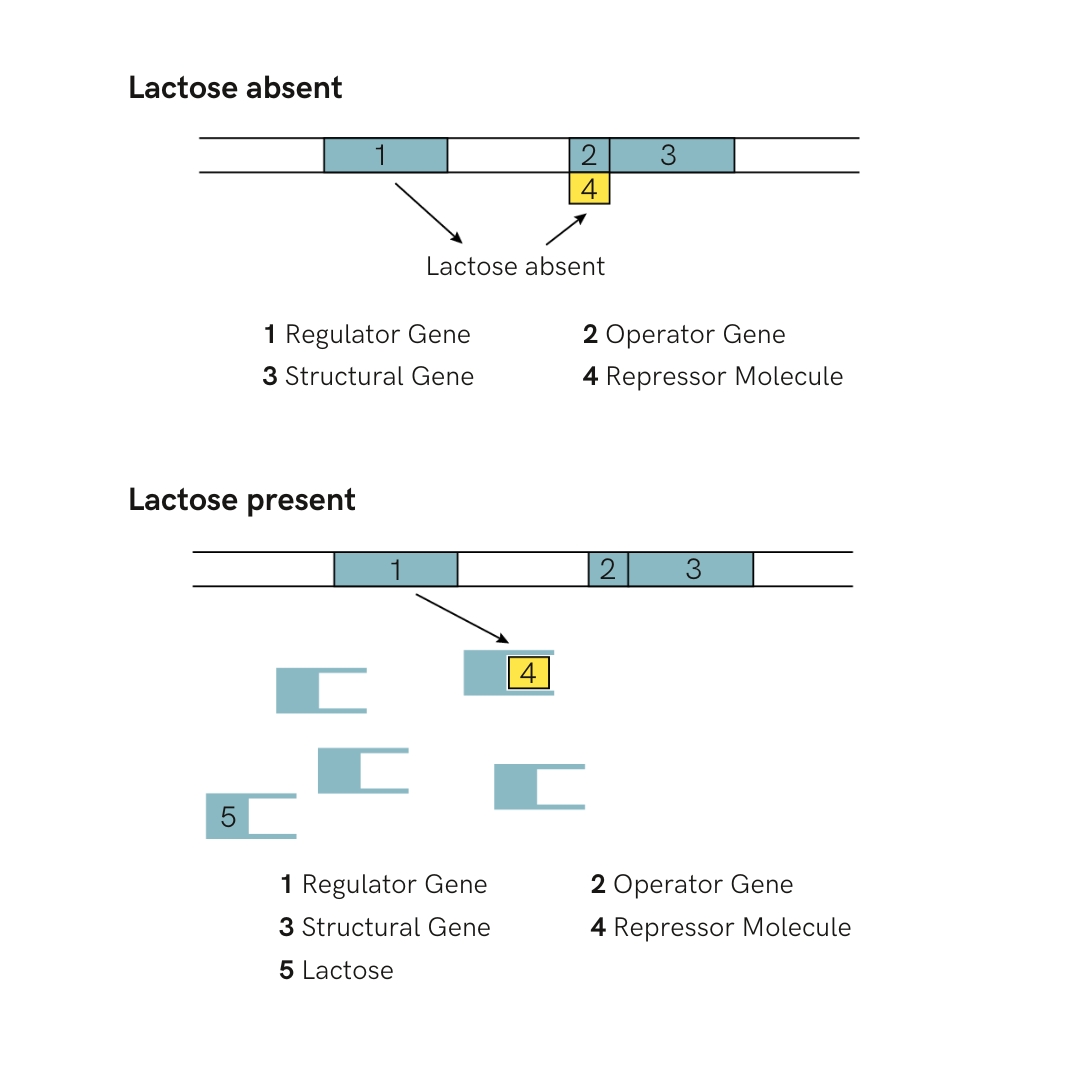
One of the most illustrative examples of Jacob and Monod’s work is the lac operon in E. coli bacteria. This operon regulates the production of enzymes necessary for the metabolisation of lactose, a sugar found in milk. Jacob and Monod showed that the expression of this operon is regulated by a repressor gene that binds to DNA and blocks transcription in the absence of lactose. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, allowing the DNA to be transcribed into mRNA and, in turn, into proteins. This discovery not only demonstrated the existence of mRNA, but also provided a general model for gene regulation in increasingly complex organisms.
Impact and recognition
The impact of Jacob and Monod’s discovery was profound and lasting. Their work not only provided a clearer understanding of gene regulation, but also influenced the development of genetic engineering and biotechnology techniques. In 1965, Jacob and Monod were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with André Lwoff, in recognition of their fundamental contributions to the understanding of the control of protein synthesis. In conclusion, François Jacob and Jacques Monod not only unlocked the mysteries of mRNA, but also provided a solid foundation on which many of today’s biological innovations were built. The discovery of mRNA has profoundly transformed precision medicine and offers new hope for patients with rare diseases. The ability to design and use mRNA to encode specific proteins allows the development of personalised therapies that directly target these RNA molecules. Rather than just treating symptoms, mRNA-based therapies can correct the underlying genetic defect, offering a more direct and effective solution. Sources: The Lac operon of Escherichia coli and the birth of molecular genetics – General and Family MedicineGene Action – Operon Hypothesis – Biology Online Tutorial
Biology y phylosophy. .
Imágenes: Nobel de Medicina: Jacques Monod, uno de los fundadores de la biología molecular y descubridor del mecanismo del mecanismo de la regulación de la expresión genética – Revista Si crees innovas
How Does Escherichia Coli Contaminate?

 Español
Español