In this second issue of #DiscoveringOligonucleotides, from the OLIGOFASTX consortium we want to introduce you to RNA therapeutics. In the field of medicine, RNA therapies stand as pioneers, offering new approaches and promising advances in the treatment of diseases hitherto thought unattainable.
RNA therapies operate at the most fundamental level of genetic information, using different molecules to address various medical conditions. Two prominent approaches are mRNA therapy and RNA interference (RNAi) therapy. mRNA acts as a messenger, providing precise instructions for protein synthesis, while RNAi disrupts gene expression by silencing specific genes.
Discovery of RNA molecules
The discovery of messenger RNA (mRNA) dates back to the 1960s, when scientists François Jacob and Jacques Monod proposed the operon hypothesis, revealing the role of mRNA in the transfer of genetic information. As for RNA interference therapy, recognition of its role in gene regulation earned Andrew Fire and Craig Mello the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2006.
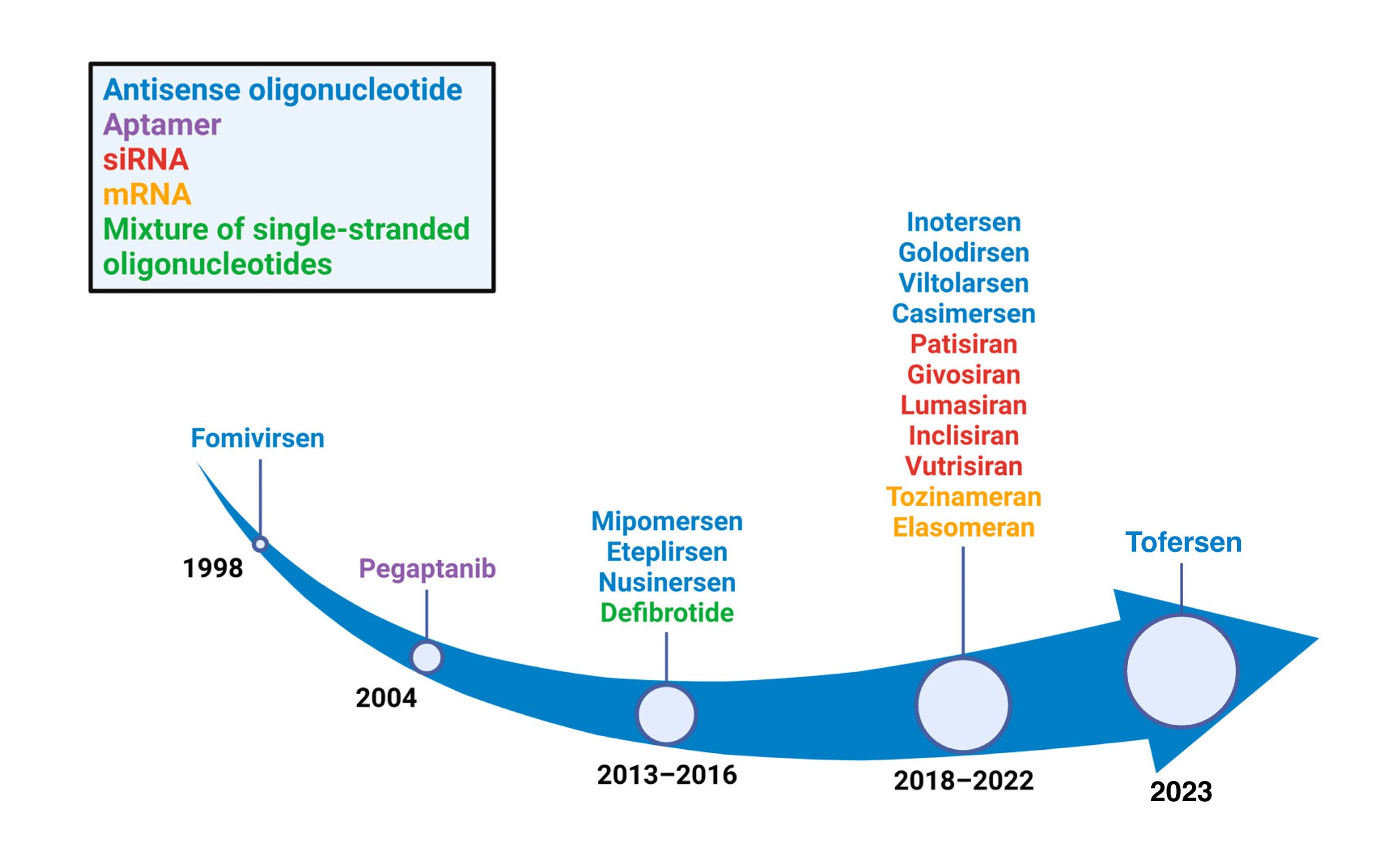
Fomivirsen: pioneer in FDA-approved RNA therapeutics
Fomivirsen, a milestone in the history of RNA-based therapies, was highlighted as the first drug of its kind to receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This innovative therapy, approved in 1998, addressed an urgent medical need by providing a solution for cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis, an eye infection that affects immunocompromised individuals, especially those with HIV.
Fomivirsen is an antisense oligonucleotide, a category of RNA molecules that specifically target complementary RNA sequences. In the case of CMV retinitis, this therapy focused on inhibiting virus replication by targeting viral RNA. Its precisely targeted mechanism of action marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of viral diseases, especially in the context of ocular infections.
This landmark achievement not only validated the feasibility of RNA-based therapies, but also paved the way for future developments in this field. Fomivirsen not only offered an effective treatment for a specific medical condition, but also set a crucial precedent for the exploration and acceptance of RNA therapies in the medical and scientific community. Since then, the approval of Fomivirsen has served as a catalyst for continued research and development of RNA therapeutics, marking an era of hope and progress in molecular medicine.
In the first article of #DiscoveringOligonucleotides we describe the oligonucleotide molecules that have been developed for these therapies. https://oligofastx.com/es/introduccion-a-los-oligonucleotidos-terapeuticos/
Diseases currently treated
RNA-based therapies have radically transformed the approach to the treatment of various diseases, presenting novel options even for those currently lacking effective therapies. Diseases amenable to RNA therapeutics include both inherited disorders, such as lysosomal storage diseases, muscular dystrophies and cystic fibrosis, and acquired diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, macular degeneration, as well as neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease, among others.
Although most of these new treatments are still in the development phase, along with innovative RNA-based vaccines, several products have already been approved for the treatment of rare diseases, such as spinal muscular atrophy and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, as well as for more common conditions, such as therapies aimed at cardiovascular prevention and the management of dyslipidemias. The future outlook anticipates the continued development of numerous RNA therapeutics, representing a new category of drugs with significant advantages due to their high specificity in mechanism of action. However, one of the main challenges in the development of these drugs lies in establishing an effective and safe delivery system capable of protecting the therapeutic RNA and facilitating its access to the site of action, thus allowing it to exert its effect in an optimal manner.
Applications and advantages applicable to the treatment of rare diseases
The flexibility and speed in the development of RNA therapeutics offer significant advantages in the treatment of rare diseases. The ability to tailor therapies to address specific genetic mutations represents a unique opportunity to address the root causes of these conditions. The hope that these therapies bring to communities affected by rare diseases is a testament to the transformative potential of precision medicine.
Ultimately, RNA therapies stand as beacons of hope for those facing as yet untreated diseases. From fundamental discoveries to current clinical applications, this dynamic field is shaping a future where genetic diseases are no longer life sentences. By embracing the potential of RNA therapies, medicine is moving toward a horizon full of possibilities for transforming lives and changing paradigms.
Sources:
RNA therapies, a present with a bright future – UPV/EHU
FDA approves first-of-its kind targeted RNA-based therapy to treat a rare disease
Approval of first ‘RNA interference’ drug – why the excitement?
Approved Cellular and Gene Therapy Products | FDA
RNA therapeutics: the key to treat rare disease?
Header Image: How does RNA know where to go in the city of the cell?

 Español
Español
